 Decrypting HTTPS-protected traffic
Decrypting HTTPS-protected traffic
Introduction
Fiddler2 includes the ability to decrypt, view, and modify
HTTPS-secured traffic for debugging purposes. The decryption feature is disabled
by default; by default, the session list will show only a  CONNECT tunnel
through which the HTTPS-encrypted bytes flow. CONNECT tunnel
through which the HTTPS-encrypted bytes flow.
Enable the traffic decryption option by clicking Tools >
Fiddler Options > HTTPS and ticking
the Decrypt HTTPS Traffic box.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: The HTTPS protocol was designed to prevent
traffic viewing and tampering. Given that, how can Fiddler2 debug HTTPS
traffic?
A: Fiddler2 relies on a "man-in-the-middle" approach to HTTPS
interception. To your web browser, Fiddler2 claims to be the secure web
server, and to the web server, Fiddler2 mimics the web browser. In order
to pretend to be the web server, Fiddler2 dynamically generates a HTTPS
certificate.
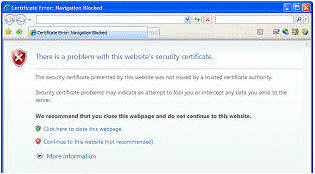
Fiddler's certificate is not trusted by your web browser (since Fiddler is
not a Trusted Root Certification authority), and hence while Fiddler2 is
intercepting your traffic, you'll see a HTTPS error message in your browser,
like so:
Q: Can I reconfigure my Windows client to trust the
Fiddler root certificate to avoid error messages in IE and Chrome, as well as
enabling logon to services like LiveID, etc?
A: Yes.
-
When you tick the "Decrypt HTTPS Traffic" checkbox in Fiddler 2.2.9+, you
will see the following prompt:
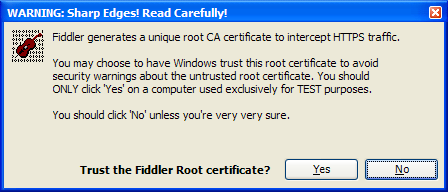
-
If you click Yes, you will see the following prompt:
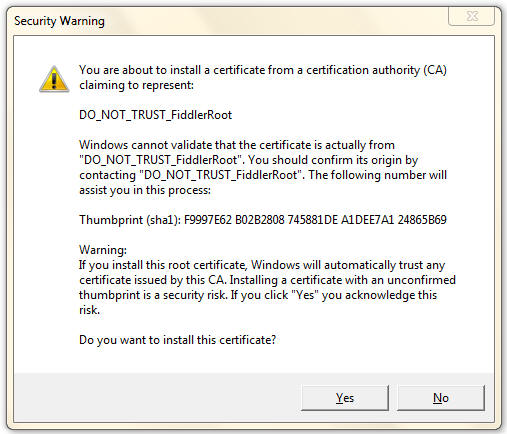
-
If you click "Yes" then Windows will trust your Fiddler Root certificate and
certificate warnings will be suppressed in any application which relies upon
the Windows Certificate Store.
Q: How do I configure Firefox to trust
the Fiddler root certificate?
A: Open Fiddler 2.2.9+. Click Tools > Fiddler Options.
Select the HTTPS tab, and click the Export Fiddler Root Certificate to
Desktop button.
In Firefox, click Tools >
Options.... Click the Advanced button at the top.
Click the Encryption tab. Click View Certificates.
Click the Authorities tab. Click Import.
Pick the .CER file from your desktop. Check the "Trust this CA to identify web sites"
checkbox.
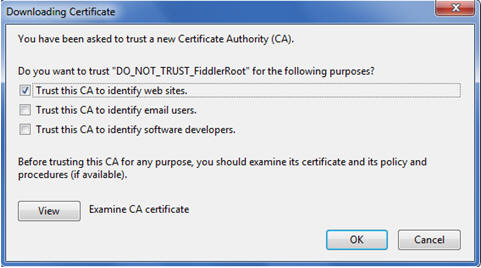
Q: I seem to always get an
endless loop of 401 Errors when visiting an internal server when HTTPS
Decryption is enabled?
A: This may be related to the Extended Protection
feature recently added to IIS. This feature binds authentication credentials to
the HTTPS-channel; since Fiddler intercepts this channel, the credentials are no
longer valid. See this
article for more information.
Q: Can
Fiddler decrypt HTTPS traffic from a different machine?
A: Yes, if you've
configured Fiddler to proxy traffic from a second computer or device, you
can decrypt that traffic, with two caveats:
-
If the client computer itself previously had run
Fiddler in HTTPS-decryption mode, all attempts to visit HTTPS pages
secured by the other computer's version of Fiddler will fail with an
unspecified certificate problem. To resolve this, remove the Fiddler
root certificate that is in the client's certificate store.
(The mismatched root certificate causes the problem, as every Fiddler
instance generates its own unique root).
-
If you want the client computer to trust the Fiddler
certificate, you will have to copy or download the Fiddler Root
certificate to the client computer and manually install it into the
Trusted Root Certification Authorities store. In Fiddler 2.3.0.9+, you
can download the Fiddler Root certificate by visiting using the URL:
http://hostnameofFiddlerMachine:8888/FiddlerRoot.cer
Q: Can
Fiddler intercept traffic from Apple iOS devices like iPad/iPhone/iPod Touch
and Android devices?
A: Yes, but these devices may not be compatible with
the default certificates Fiddler generates.
To resolve the incompatibility, you may replace Fiddler's default
certificate generator with one that generates certificates containing flags
(e.g. AKID, SKID) that are compatible with these platforms. Simply download and install the new
Certificate Maker and restart Fiddler.
Q: Can
Fiddler be configured to decrypt traffic only from certain hosts or
processes?
A:
Yes. You can do so by setting the x-no-decrypt flag on a
given session. For instance, here's a bit of script that you can put inside
OnBeforeRequest to prevent decryption of traffic to all hosts except a target
host,
if (oSession.HTTPMethodIs("CONNECT")
&&
!oSession.HostnameIs("SiteICareAbout.com"))
{
oSession["x-no-decrypt"] = "do not care."; }
or, in Fiddler
2.3.0.6 or later, you can do so by listing the hostname inside the text box Skip
Decryption for the following hosts found by clicking Tools > Fiddler Options >
HTTPS.
Alternatively, you could disable HTTPS-decryption for
traffic from an entire application (e.g. boring.exe) using a rule like
this inside OnBeforeRequest:
if
(oSession.HTTPMethodIs("CONNECT") && oSession["X-PROCESSINFO"] &&
oSession["X-PROCESSINFO"].StartsWith("outlook"))
{
oSession["x-no-decrypt"] = "boring process";
}
Q: Does Fiddler2 demonstrate a flaw in HTTPS?
A: No. HTTPS relies on certificates in order to secure web
traffic. Web browsers prevent man-in-the-middle attacks by relying upon
Trusted Root Certification authorities to issue certificates that secure the
traffic. As designed, web browsers will show a warning when traffic is not
protected by a certificate issued by a trusted root.
Q: Does Fiddler2 support sites that require client
certificates?
A: Yes, Fiddler 2.1.0.3 and later support client
certificates. See Attaching
Client Certificates for more information.
Q: Is Fiddler2 the only tool that debugs
HTTPS traffic?
A: No. There are a number of other free tools which offer this
capability, including the Charles and Burp proxies, written with Java.
< Back to Help Homepage
©2013 Telerik
| 
 Get the NEW book!
Get the NEW book!